Zinngrebe, J;
Walczak, H;
(2017)
TLRs Go Linear – On the Ubiquitin Edge.
Trends in Molecular Medicine
, 23
(4)
pp. 296-309.
10.1016/j.molmed.2017.02.003.

Preview |
Text (Article)
Walczak_main file_revised_TMM_JZ and HW.pdf - Accepted Version Download (294kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure 1]](https://discovery-pp.ucl.ac.uk/10049802/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Walczak_Figure%201.png) 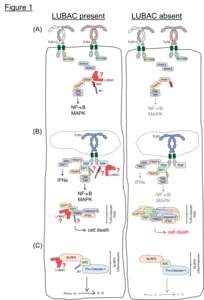 Preview |
Image (Figure 1)
Walczak_Figure 1.png - Accepted Version Download (995kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure 2]](https://discovery-pp.ucl.ac.uk/10049802/12.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Walczak_Figure%202.png) 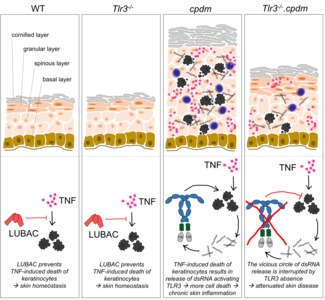 Preview |
Image (Figure 2)
Walczak_Figure 2.png - Accepted Version Download (1MB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of Figure 3]](https://discovery-pp.ucl.ac.uk/10049802/17.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Walczak_Figure%203.png) 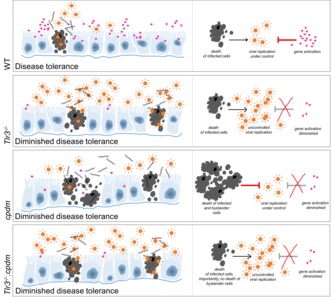 Preview |
Image (Figure 3)
Walczak_Figure 3.png - Accepted Version Download (1MB) | Preview |
Abstract
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are crucial in protecting the host from pathogens. However, their exact role in disease remains incompletely understood. TLR signaling is tightly controlled because too little or too much TLR activation can result in immunodeficiency or autoinflammation, respectively. There is increasing evidence that linear ubiquitination, mediated by the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC), plays a pivotal role in the regulation of TLR signaling. Recent advances have identified an intricate interaction between LUBAC and TLRs, with immunological consequences for infection and the development of autoinflammation in the host. We propose that defective linear ubiquitination contributes to TLR-mediated disease pathogenesis and that perturbed TLR signaling contributes to the phenotype observed in inherited LUBAC deficiency in humans and mice.
Archive Staff Only
 |
View Item |


