Slade, E;
Keeney, E;
Mavranezouli, I;
Dias, S;
Fou, L;
Stockton, S;
Saxon, L;
... Kendall, T; + view all
(2018)
Treatments for bulimia nervosa: a network meta-analysis.
Psychological Medicine
, 48
(16)
pp. 2629-2636.
10.1017/S0033291718001071.

Preview |
Text
Serpell_BN NMA_Slade et al (main paper).pdf - Accepted Version Download (417kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Serpell_BN NMA_Slade et al (Figure 1).pdf - Accepted Version Download (151kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Serpell_BN NMA_Slade et al (Figure 2)_colour.pdf - Accepted Version Download (101kB) | Preview |
![[thumbnail of BN NMA_Slade et al (Figure 3)_colour.png]](https://discovery-pp.ucl.ac.uk/10049405/5.hassmallThumbnailVersion/BN%20NMA_Slade%20et%20al%20%28Figure%203%29_colour.png) 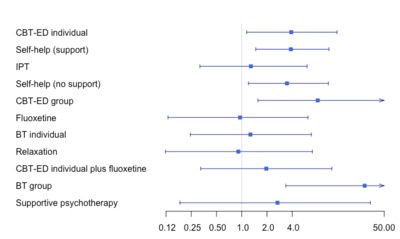 Preview |
Image
BN NMA_Slade et al (Figure 3)_colour.png - Accepted Version Download (34kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Serpell_BN NMA_Slade et al (Table 1).pdf - Accepted Version Download (114kB) | Preview |
Preview |
Text
Serpell_BN NMA_Slade et al (Table 2).pdf - Accepted Version Download (146kB) | Preview |
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Bulimia nervosa (BN) is a severe eating disorder that can be managed using a variety of treatments including pharmacological, psychological, and combination treatments. We aimed to compare their effectiveness and to identify the most effective for the treatment of BN in adults. METHODS: A search was conducted in Embase, Medline, PsycINFO, and Central from their inception to July 2016. Studies were included if they reported on treatments for adults who fulfilled diagnostic criteria for BN. Only randomised controlled trials (RCTs) that examined available psychological, pharmacological, or combination therapies licensed in the UK were included. We conducted a network meta-analysis (NMA) of RCTs. The outcome analysed was full remission at the end of treatment. RESULTS: We identified 21 eligible trials with 1828 participants involving 12 treatments, including wait list. The results of the NMA suggested that individual cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) (specific to eating disorders) was most effective in achieving remission at the end of treatment compared with wait list (OR 3.89, 95% CrI 1.19-14.02), followed by guided cognitive behavioural self-help (OR 3.81, 95% CrI 1.51-10.90). Inconsistency checks did not identify any significant inconsistency between the direct and indirect evidence. CONCLUSIONS: The analysis suggested that the treatments that are most likely to achieve full remission are individual CBT (specific to eating disorders) and guided cognitive behavioural self-help, although no firm conclusions could be drawn due to the limited evidence base. There is a need for further research on the maintenance of treatment effects and the mediators of treatment outcome.
Archive Staff Only
 |
View Item |


